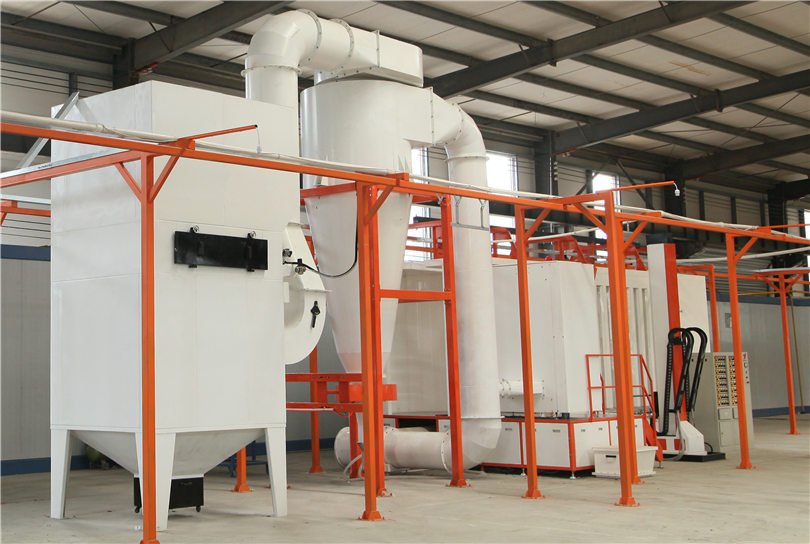
Electrophoretic coating line is a kind of surface coating technology widely used in modern industrial production, which can provide high-quality coating protection, prolong service life and enhance the appearance of products.
The electrophoresis tank is an important and indispensable part of the electrophoresis coating line.
In this article, we will introduce in-depth the electrophoresis tank in the electrophoresis coating line, including its principle, types and application areas.
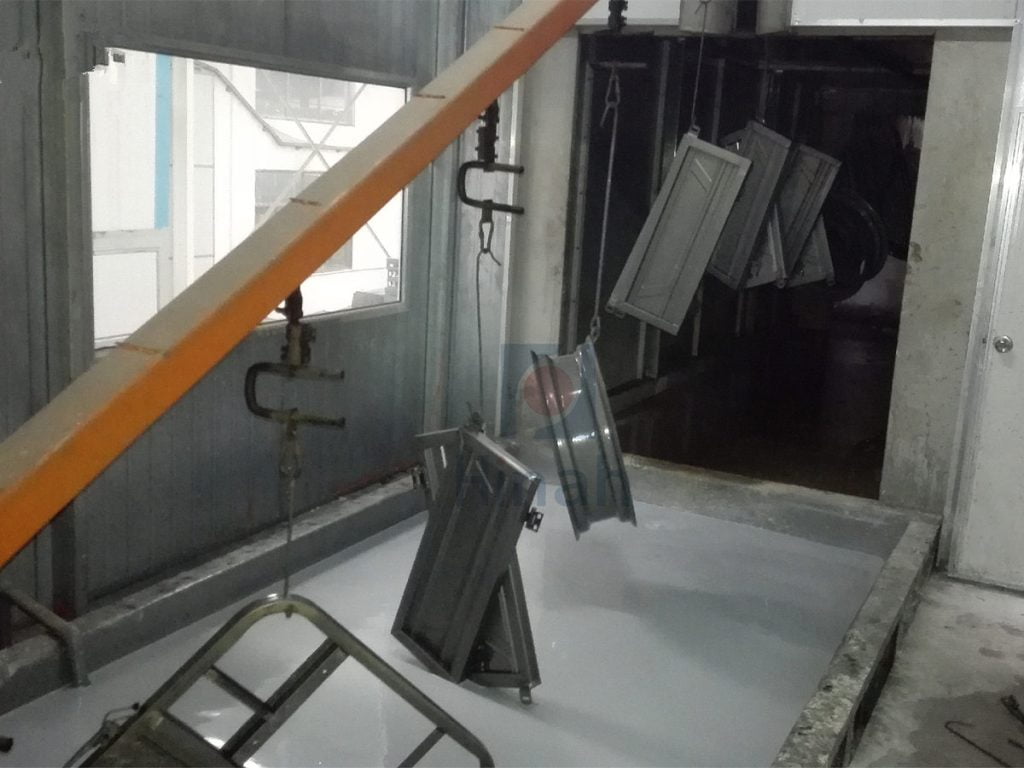


I. Basic Principle of Electrophoretic Tank
Electrophoretic coating is a process that uses an electric field to form a uniform and durable coating on the surface of conductive objects. An electrophoretic bath is the core equipment in an electrophoretic coating line, and its operating principle is based on electrochemical reactions and electric field action. The following are the basic principles of an electrophoresis tank:
1. Electrochemical reaction
In an electrophoresis tank, the surface of the workpiece is immersed in a solution of electrophoretic paint, usually water-based. The particles in the paint are charged, usually negatively. The surface of the workpiece is then connected to an anode (positive electrode), and the paint particles are directed towards the surface of the workpiece as current passes through the electrophoresis tank.
2. Electric field effect
The electrophoresis tank is equipped with an internal electrode system that creates an electric field by applying a voltage. This electric field attracts the charged paint particles to the surface of the workpiece and causes them to be deposited uniformly on the surface of the workpiece. This process is known as electrophoretic deposition, where the paint particles are deposited on the surface of the workpiece and form a uniform coating.
3. Coating Curing
Once the coating particles have been deposited on the surface of the workpiece, the coating usually needs to be cured. This can be achieved by methods such as baking or UV curing. Once cured, the coating will be strong and have excellent adhesion.
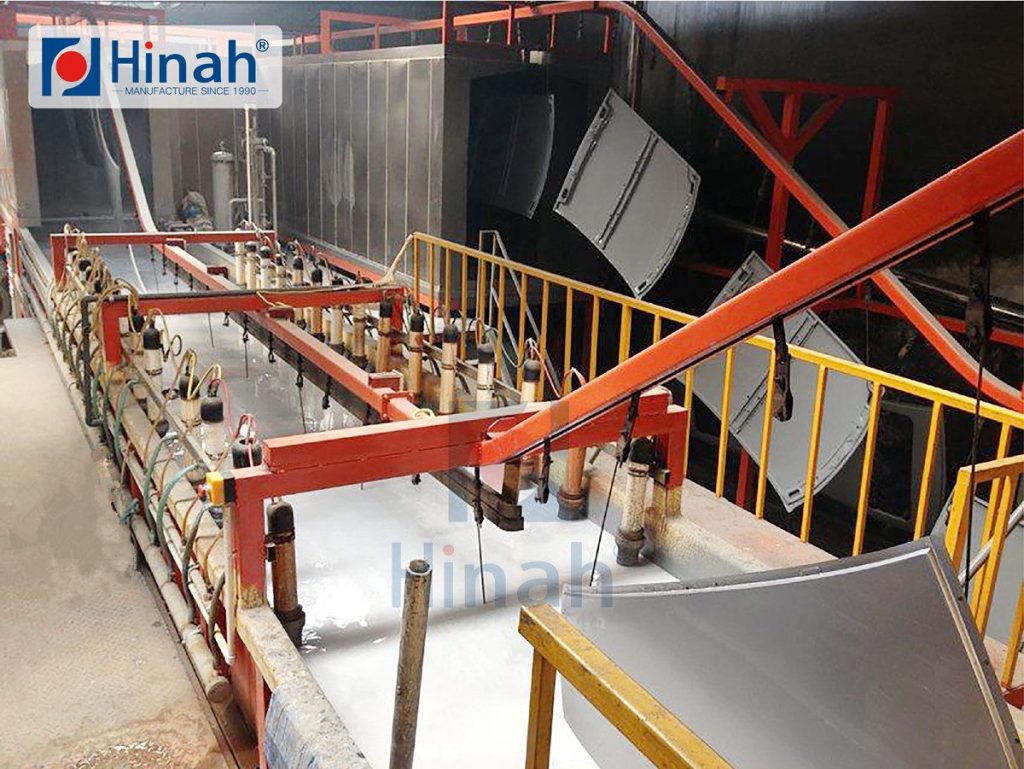
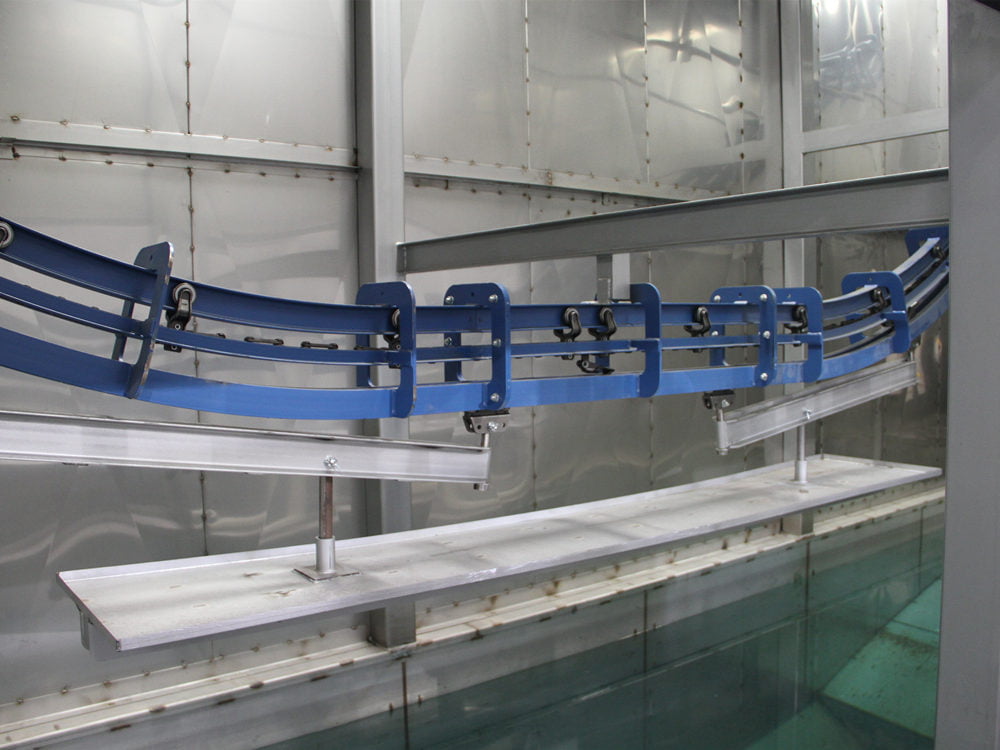


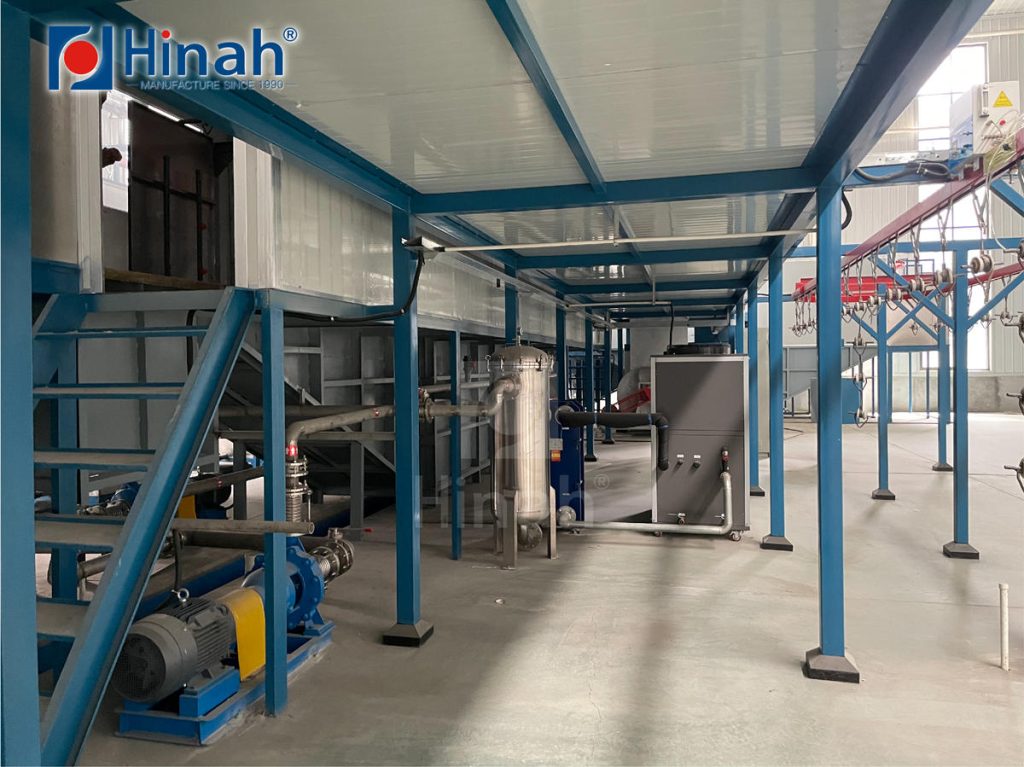
II. Composition of an electrophoretic bath
An electrophoresis tank is a key component of an electrophoresis coating line, and its composition usually includes the following major components:
1. Tank:
The tank is the main container of the electrophoresis tank and is usually made of corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or plastic. The size and shape of the tank will vary according to the size and shape of the workpiece to be coated.
2. Electrode System:
The electrode system consists of anode and cathode, which are the key components for establishing the electric field. The anode is usually connected to the positive terminal of the power source, while the cathode is connected to the negative terminal of the power source. The electrodes are usually made of a conductive material, such as stainless steel.
3. Power Supply:
The power supply provides the required voltage and current to establish the electric field in the tank. By adjusting the parameters of the power supply, the uniformity and thickness of the coating can be controlled.
4. Coating Solution:
The coating solution is the paint solution in the electrophoresis tank, usually water-based electrophoresis coatings. These coatings contain particles that are electrically charged and can be directed to the surface of the workpiece under the action of an electric field.
5. Agitation System:
The agitation system is used to maintain the uniformity of the coating liquid and to prevent particle deposition or delamination. This can be achieved by mechanical agitation or bubble injection.
6. Temperature Control System:
The temperature of the coating liquid can affect the quality and uniformity of the coating. Therefore, electrophoresis tanks are usually equipped with a temperature control system to ensure that the electrophoresis coating is carried out at the proper temperature.
7. pH Adjustment System:
The pH value of the coating liquid is also a key factor affecting the quality of the coating. pH adjustment system is used to maintain the ideal pH range of the coating liquid.
8. Automation Control System:
Modern electrophoresis tanks are usually equipped with an automation control system that monitors and adjusts electric field parameters, coating time and temperature to ensure consistent coating quality.
9. Drainage System:
After the electrophoresis coating is completed, it is usually necessary to remove the excess coating liquid. Drainage systems recycle or dispose of the coating fluid to minimise waste.
These components work together to ensure the efficient operation of the electrophoretic tank during the electrophoretic coating process, resulting in uniform and durable coating coverage. The design and configuration of an electrophoresis tank will vary depending on the requirements of the specific application and the characteristics of the workpiece.
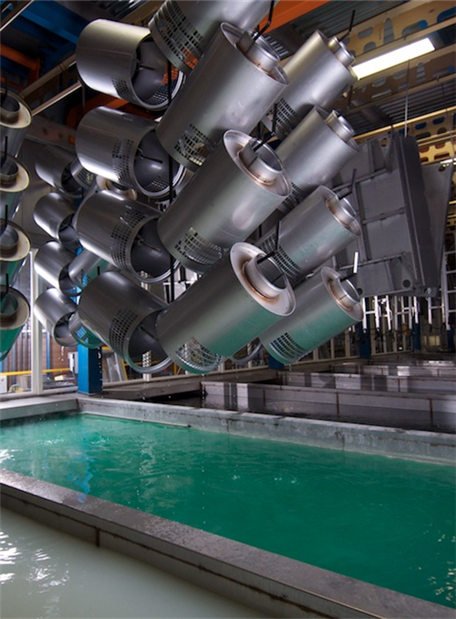
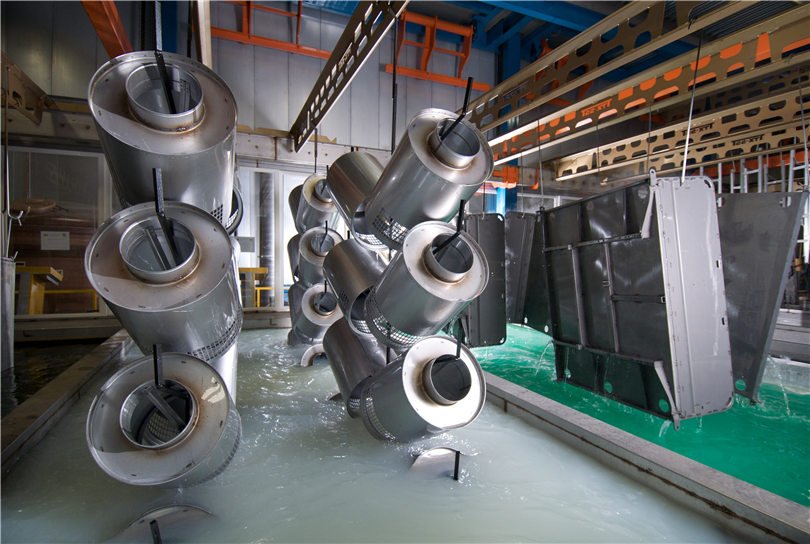


III. Types of Electrophoresis Tanks
There are various types of electrophoresis tanks in an electrophoretic coating line, each suitable for different applications and requirements. The following are some common types of electrophoresis tanks:
1. Continuous Electrophoresis Tank
Continuous electrophoresis baths are typically used in high-volume production environments. The workpieces move on a continuous transport system and as they pass through the tank, the electrophoretic coating adheres uniformly to their surfaces. This type of tank is suitable for coating large quantities of parts.
2. Batch Electrophoresis Tank
The batch electrophoresis tank is suitable for small batch production or customised coating requirements. The workpieces are usually placed in the tank and then subjected to the electrophoretic coating process. This type of tank is more flexible and is suitable for a variety of different shapes and sizes of workpieces.
3. Rotary Electrophoresis Tank
Rotary tanks use a rotating mechanism to rotate the work piece to ensure even coverage of the surface. This type of tank is usually used for coating workpieces that require a high degree of uniformity, such as automotive parts.
4. Spray Electrophoresis Tank
Spray type electrophoresis tanks achieve coating by spraying paint onto the surface of the workpiece. This method is suitable for applications that require fast coating, but usually requires more paint.
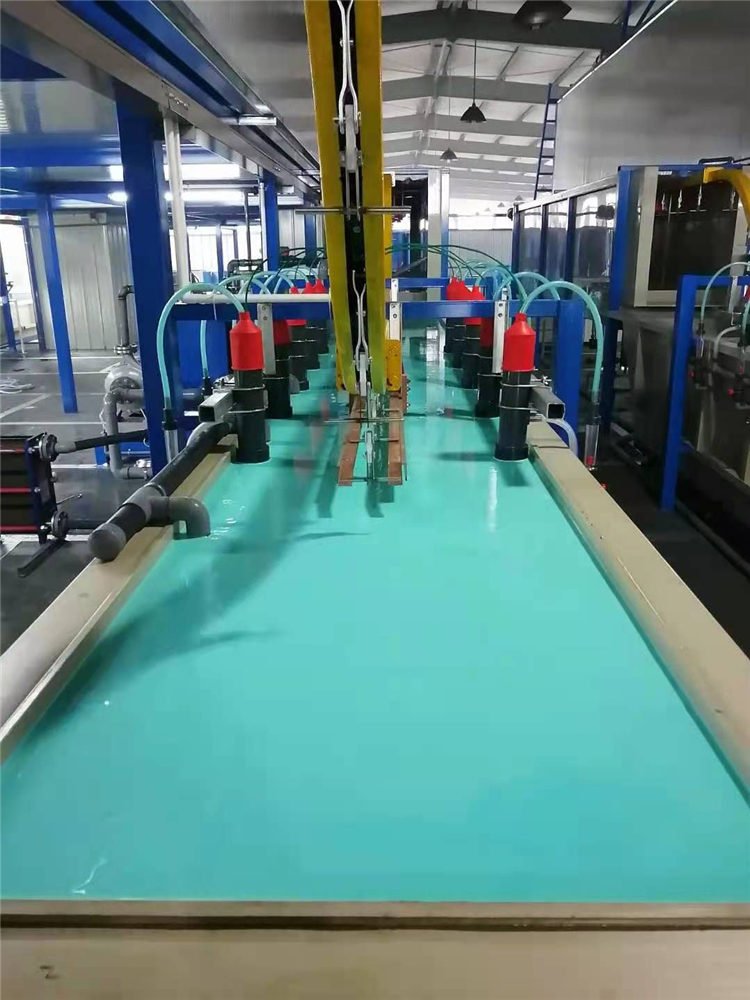

IV. Application areas of electrophoresis tanks
Electrophoresis tanks in electrophoretic coating lines are widely used in a number of industries, including automotive manufacturing, appliance manufacturing, metal fabrication, and construction. The following are some of the major application areas:
1. Automobile manufacturing
Electrophoretic coating plays a key role in automobile manufacturing, which can provide anti-corrosion and wear-resistant coating for the car shell and improve the appearance quality and life of the car.
2. Metal Manufacturing
The metal manufacturing industry uses electrophoretic coating to prevent rust and corrosion on metal products. This includes pipes, guardrails, steel structures, etc.
3. Appliance Manufacturing
Electrophoretic coating is also used to coat home appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, microwave ovens, etc. to provide an attractive and corrosion-resistant finish.
4. Construction
The construction industry uses electrophoretic coating to protect building structures, such as steel beams and aluminium window frames, from harsh weather conditions.
V. Conclusion
To summarise, the electrophoretic bath is an integral part of the E-coating line, which achieves uniform deposition of coatings through the action of an electric field and an electrochemical reaction, and is widely used in a number of industrial sectors to provide high quality, durable coating protection.
The continuous development of electrophoretic coating technology will bring more innovation and improvement to industrial production.







